VPN is widely used in enterprises. Its purpose is to establish more secure connections between different branches or between employees on business trips and the enterprise office, and then perform other access operations based on this link, such as FTP, CRM, ERP, WWW, financial system, Internet telephone, etc. However, if you don’t have such high requirements and just want to provide services externally, you can consider using port mapping.
Today we will only discuss one type of port mapping/forwarding, which is also considered as DNAT. To allow Internet users to access servers on the Intranet, you need to perform port mapping on the Router of the egress gateway so that services on the Intranet can be accessed through the public IP address of the egress gateway plus the service port number. Therefore, the prerequisite for port mapping is that the Router connecting to the Internet through an ADSL broadband Router must have a dynamic or fixed Public IP address, or obtain a Public IP address assigned by the carrier through dial-up Internet access.
Port mapping is to map a port of the IP address of an extranet host to a machine on the Intranet to provide corresponding services. When a user accesses this port of the IP, the server automatically maps the request to a machine within the corresponding LAN. Port mapping can be dynamic or static.
Generally speaking, port mapping is to map the Intranet (LAN) IP address of a host to a public network (WAN) IP address. When a user accesses a port on a host that provides the port mapping, the server forwards the request to a host that provides the specific service on the LOCAL LAN. The port mapping function can also be used to map multiple ports of an external IP address machine to different ports on different Intranet machines. The port mapping function can also perform some agent-specific functions, such as proxy for POP, SMTP, TELNET, and other protocols. In theory, the mapping between 65535 (total number of ports) and 1024 (reserved number of ports) =64511 ports can be provided.
Port mapping is a common operation during router configuration. The purpose is to change ports for different services to achieve more flexible applications.
As the following show, Any device which is capable of reaching the Internet can access the IP camera on site A (192.168.2.2:80) via port mapping(10.5.30.180:8001).

Here we’re configuring the Router at site A.
After login to the Web UI, you can navigate to Status->Network Connections to check the static IP of the device. The cellular Static IP of my IR302 is 10.5.30.180.

Then you can navigate to Status->Device List to check the connected device and their assigned IP addresses. The IP of my IP camera is 192.168.2.2.

Firewall-> Port Mapping
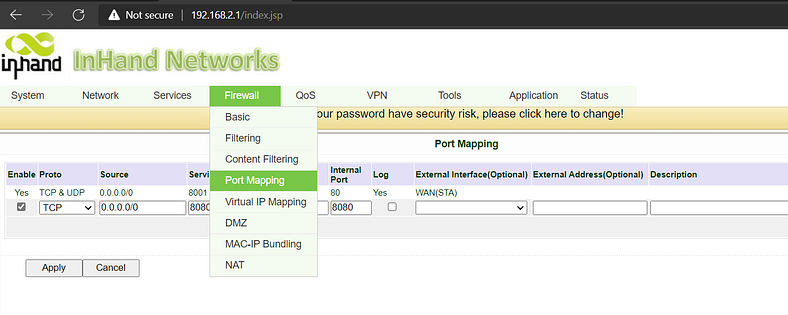
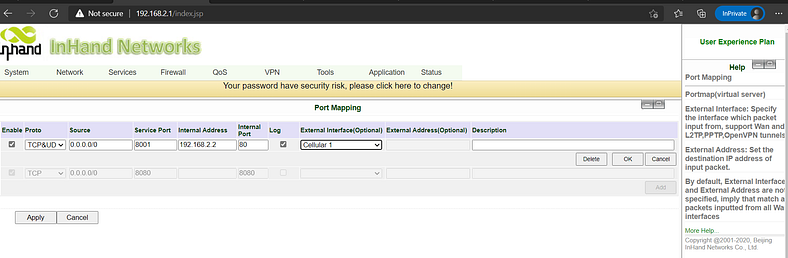
Source IP: 0.0.0.0/0 (allow any IP from the external port- Cellular 1)
Service port: the service ports open on the router.Internal Address: IP addresses of the lower-end devices.Internal ports: service port of the lower-end devices.
For example, here is when any external address accesses port 8001 of 10.5.30.180 (assume it is dial-up assignment), it actually accesses port 80 of 192.168.2.2 (lower side IP camera)
the PC at site B can enter 10.5.30.180:8001 to access the IP camera on site A.